- A Guide to Tuberous Breasts - Diagnosis, Treatment and Recovery
- Take our Plastic Surgery Quiz to find out if you'd be a good candidate for cosmetic surgery.
- Anatomy of Tuberous Breasts
- Causes of Tuberous Breasts
- Diagnosing Tuberous Breasts
- Surgical Options for Tuberous Breast Correction
- Breast Augmentation
- Types of Implants
- Download the Breast Augmentation Guide
- Tissue Expansion Techniques
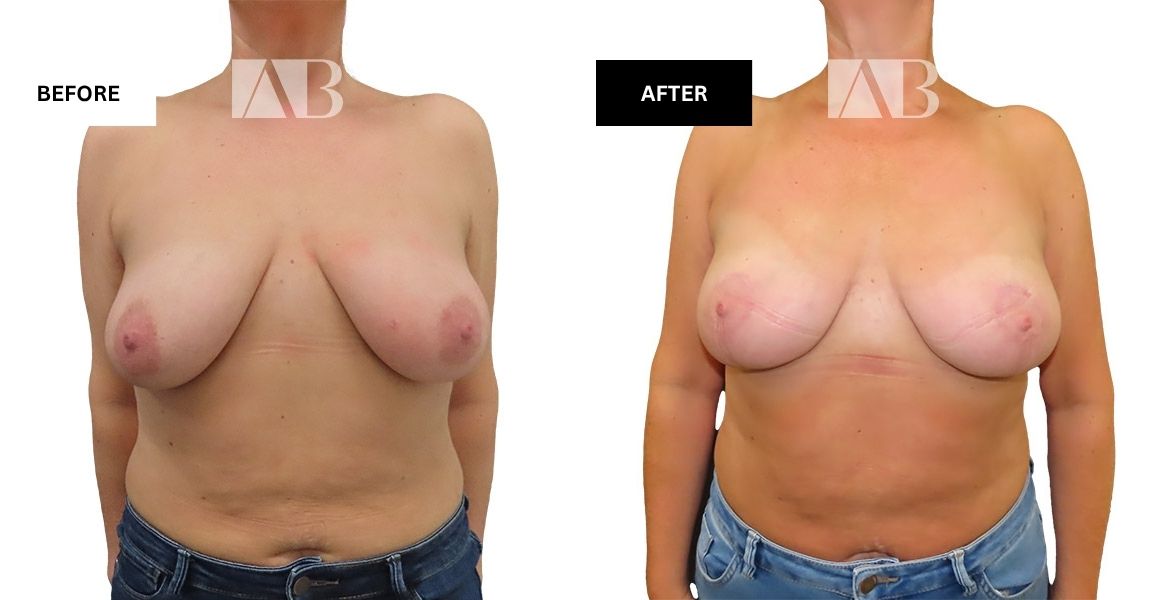
- Breast Augmentation Before and After Photos
- Breast Uplift (Mastopexy) to Correct Tuberous Breasts
- Download the Breast Uplift Guide
- Fat Grafting for Tuberous Breasts
- Breast Lift Before and After Photos
- Combined Procedures
- FAQs about Tuberous Breasts
- Further Reading about Breast Augmentation with Consultant Plastic Surgeon Anca Breahna
A Guide to Tuberous Breasts – Diagnosis, Treatment and Recovery
Tuberous breasts represent a condition not widely recognised outside of professional medical circles, yet it affects a significant number of individuals. This condition, often identified by its unique physical characteristics, involves underdeveloped breasts that can present a range of appearances, from mild to more pronounced forms. Typically, this condition becomes apparent during puberty, when breasts begin to develop.
The defining features of tuberous breasts include a constricted breast base, which leads to a more tubular rather than rounded shape, herniation of breast tissue through the areola, leading to puffiness, and asymmetry between the breasts.
Many assume that variations in breast size and shape are standard, not recognising when these characteristics might indicate a tuberous breast condition. Do You Have Pointy Boobs? They Could Be Tuberous Breasts explores the telltale signs in more detail. Understanding these signs is critical for seeking appropriate advice and treatment options. Consultant Plastic Surgeon Anca Breahna performs tuberous breasts surgery to correct this condition.
Take our Plastic Surgery Quiz to find out if you’d be a good candidate for cosmetic surgery.
Anatomy of Tuberous Breasts
The anatomical peculiarities of tuberous breasts set them apart from more typical breast development. At the heart of this condition lies the constriction of the breast base, the area directly over the chest wall, which restricts normal outward and downward growth. This constriction results in a more tubular or narrow breast shape, significantly differing from the rounded appearance typically expected.
One of the most notable variations in tuberous breasts is the degree of herniation observed in the areolar region. This refers to breast tissue pushing forward through the areola, leading to an enlarged and puffy appearance. Additionally, asymmetry is often a hallmark of this condition, with one breast developing differently from the other, sometimes in a pronounced manner. These characteristics not only influence physical appearance but also how bras and clothing fit, potentially leading to discomfort during everyday activities.
Causes of Tuberous Breasts
The aetiology of tuberous breasts remains an area of active research, with current understanding pointing towards a combination of genetic and developmental factors. This condition manifests during puberty, a critical period of breast development, suggesting that the underlying causes may interfere with normal breast tissue growth and expansion.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of tuberous breasts. Although the exact genetic markers or inheritance patterns are not fully understood, it is observed that women with tuberous breasts often have a family history of similar breast development issues. This genetic link underscores the importance of a detailed family medical history during the diagnostic process.
Developmental anomalies during the breast development phase are another critical factor. The breast base’s constriction prevents the normal expansion of breast tissue, leading to the characteristic tubular shape. This constriction is believed to result from an abnormality in the connective tissue development within the breast, which may be influenced by genetic predispositions.
The precise interplay between these factors is complex and individualised, meaning that each case of tuberous breasts may have a unique set of underlying causes. Despite this complexity, understanding the potential causes is fundamental for developing targeted treatment strategies. It also provides reassurance to individuals that their condition results from factors beyond their control, rather than lifestyle choices or environmental influences.
Diagnosing Tuberous Breasts
The diagnosis of tuberous breasts is a process that requires a keen eye for detail and a deep understanding of the condition’s anatomical characteristics. It usually involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging techniques.
During a clinical examination, Anca will assess the shape, size, and symmetry of the breasts, paying particular attention to the base of the breast, the presence of herniation through the areola, and any signs of asymmetry. These physical characteristics are essential in differentiating tuberous breasts from other variations in breast shape and size. It is a sensitive process, conducted in a respectful and supportive environment, ensuring that you feel comfortable and understood.
Imaging techniques, such as mammography or ultrasound, play a supportive role in the diagnosis. These methods can provide detailed insights into the internal structure of the breast, offering a clearer view of the tissue distribution and any underlying abnormalities that might not be apparent through a physical examination alone. In certain cases, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be recommended to gain a comprehensive understanding of the breast’s internal structure. These imaging studies are important for planning any potential treatments and ensuring that any interventions are tailored to your specific needs.
Surgical Options for Tuberous Breast Correction
Correcting tuberous breasts surgically requires a customised approach, taking into account the unique challenges presented by this condition. The primary goal is to reshape the breasts into a more rounded form, correct areolar herniation, and achieve symmetry. Various surgical techniques are employed, either singularly or in combination, to address these aspects. Here’s an overview of the primary surgical options:
Breast Augmentation
Breast enlargement is an option for the surgical correction of tuberous breasts, offering you the opportunity to achieve a more rounded and symmetrical breast shape. This procedure involves the insertion of implants, which can significantly improve both the size and contour of the breasts.
Types of Implants
The choice of implants plays a role in achieving the desired aesthetic outcome. There are primarily two types of breast implants: saline and silicone. Saline implants consist of a silicone shell filled with sterile saltwater. They are inserted empty and then filled to the desired volume once in place, allowing for adjustable size and a smaller incision. Silicone implants, on the other hand, are pre-filled with a silicone gel that closely mimics the feel of natural breast tissue. They are known for their ability to provide a more natural look and feel but require a slightly larger incision for placement.
In the context of tuberous breast correction, the choice between saline and silicone implants will be guided by several factors, including your body type, the degree of breast tissue available, and personal preference. Anca will provide guidance on the most suitable type of implant based on these factors and the desired outcome.
Download the Breast Augmentation Guide

Tissue Expansion Techniques
Tissue expansion is a technique used in various reconstructive surgery procedures, including the correction of tuberous breasts. This method is particularly beneficial for individuals who have limited breast skin or where the skin is too tight to accommodate an implant immediately. Tissue expansion allows for a gradual enlargement of the breast area to create sufficient space for an implant or to enhance the natural appearance of the breast.
The Process of Tissue Expansion
The tissue expansion process begins with the surgical insertion of a balloon expander beneath the skin and muscle of the breast area. This expander is then gradually filled with saline over a period of weeks or months, slowly stretching the skin and tissue. The rate of expansion and the total volume of saline added are carefully controlled by Anca, based on your tissue response and the desired outcome.
Once the skin has been stretched adequately, a second surgery is performed to remove the expander and insert the breast implant. In some cases, the expansion process can also help improve the symmetry between breasts, making it a versatile tool in the correction of tuberous breasts.
Tissue expansion offers several advantages, particularly for women with tuberous breasts. It allows for a more controlled and gradual stretching of the breast tissue and skin, which can be crucial in achieving a natural-looking breast shape. This method is especially beneficial for women with severe constriction at the breast base, as it facilitates the creation of a more rounded breast contour.
Additionally, tissue expansion can minimise the risk of complications associated with placing a large implant in a constrained space, such as excessive tension on the skin or the unnatural appearance of the breast. By allowing the skin and tissue to adjust gradually, tissue expansion can lead to a more aesthetically pleasing and comfortable outcome.
Breast Augmentation Before and After Photos
Breast Uplift (Mastopexy) to Correct Tuberous Breasts
A breast lift, or mastopexy, is another option for the surgical correction of tuberous breasts. This procedure is designed to raise and firm the breasts by removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissue. For those with tuberous breasts, a mastopexy can address issues such as sagging or elongated shapes, and position the nipple and areola in a more aesthetically pleasing manner.
Women with tuberous breasts may find that a breast lift is especially beneficial, as it can directly address the shape and position issues associated with this condition. When the tuberous deformity includes significant sagging or a downward orientation of the nipple, a mastopexy can offer significant improvements in the appearance of the breasts, making them appear more rounded and symmetrical.
Combining a breast lift with other procedures, such as breast augmentation, is common in treating tuberous breasts. This combination allows Anca to address both the volume and the positioning of the breasts simultaneously, providing a complex correction of the condition.
Download the Breast Uplift Guide

Fat Grafting for Tuberous Breasts
Fat grafting, also known as autologous fat transfer, has emerged as a valuable technique in the correction of tuberous breasts, offering a more natural alternative or complement to traditional implants. This procedure involves harvesting fat from one part of the body through liposuction, processing it, and then injecting it into the breasts to improve their size, shape, and symmetry. For women with tuberous breasts, fat grafting can address some of the condition’s unique challenges, providing a tailored approach to breast enhancement.
Fat grafting offers several benefits in the context of tuberous breast correction. It uses your own tissue, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or rejection. Additionally, the technique can provide a more natural look and feel compared to synthetic implants, appealing to those seeking subtle enhancements or those concerned about the long-term implications of implants.
This technique also allows for the correction of specific areas of the breast that may be difficult to address with implants alone, such as filling in constricted bases or improving breast symmetry. Moreover, since fat grafting does not require large incisions, it is associated with a shorter recovery time.
Breast Lift Before and After Photos
Combined Procedures
Often, a combination of the above techniques is necessary to achieve the best results in tuberous breast correction. Anca may combine breast augmentation with a lift, or use tissue expansion followed by implants, depending on your specific needs. The combination approach allows for the correction of the tuberous deformity, addressing both the size and shape of the breasts as well as any asymmetry.
Surgical correction of tuberous breasts is highly individualised, requiring a skilled and experienced surgeon to achieve optimal results. The choice of procedure(s) will depend on the severity of the tuberous deformity, the condition of the breast tissue and your aesthetic goals. With careful planning and execution, surgical correction can significantly improve the appearance of the breasts, offering you a renewed sense of comfort and satisfaction with your body.
FAQs about Tuberous Breasts
How are tuberous breasts diagnosed?
Diagnosing tuberous breasts typically involves a clinical examination by a healthcare professional, where the shape, size, and symmetry of the breasts are assessed. Imaging techniques such as mammography or ultrasound may also be employed to gain a detailed view of the breast’s internal structure, helping to confirm the diagnosis and plan potential treatments.
What treatment options are available for tuberous breasts?
While there are non-surgical options for managing tuberous breasts, surgical correction is often recommended for significant improvement. Surgical options include breast augmentation with implants, tissue expansion techniques, breast lift (mastopexy), and fat grafting. The choice of surgery or combination of surgeries depends on your specific anatomy, the severity of the condition, and personal preferences.
What can be expected during the recovery from tuberous breast correction surgery?
Recovery varies depending on the surgical procedure performed but generally involves a period of rest, with limited activity to allow for healing. Immediately after surgery, experiencing pain, swelling, and bruising is common, with most patients able to return to light activities within a few weeks. Full recovery and seeing the final results of the surgery can take several months, during which follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring progress and addressing any concerns.
Medical References
- Tuberous Breast Management (PubMed) – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9760626/
- Review of Tuberous Breast Deformity (PubMed) – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9187173/
- Aesthetic Reconstruction of the Tuberous Breast Deformity (Oxford Academic) – https://academic.oup.com/asj/article/30/5/680/255249
- Tubular Breasts: What They Are, Causes & Treatment (Cleveland Clinic) – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/tubular-breasts
- The tuberous breast revisited (Science Direct) – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1748681507000174
Further Reading about Breast Augmentation with Consultant Plastic Surgeon Anca Breahna
- Read more about Breast Augmentation with Mentor Breast Implants
- Read more about What is Breast Augmentation Surgery?
- Read more about Plastic Surgery Procedures to Get Bigger Breasts
- Read more about Causes and Treatments for Tuberous Breasts




 Ms Anca Breahna, PhD, MSc, FEBOPRAS, FRCS (Plast) is a highly regarded Consultant Plastic Surgeon specialising in the field of Aesthetic and Reconstructive Plastic Surgery. Anca performs a range of
Ms Anca Breahna, PhD, MSc, FEBOPRAS, FRCS (Plast) is a highly regarded Consultant Plastic Surgeon specialising in the field of Aesthetic and Reconstructive Plastic Surgery. Anca performs a range of 